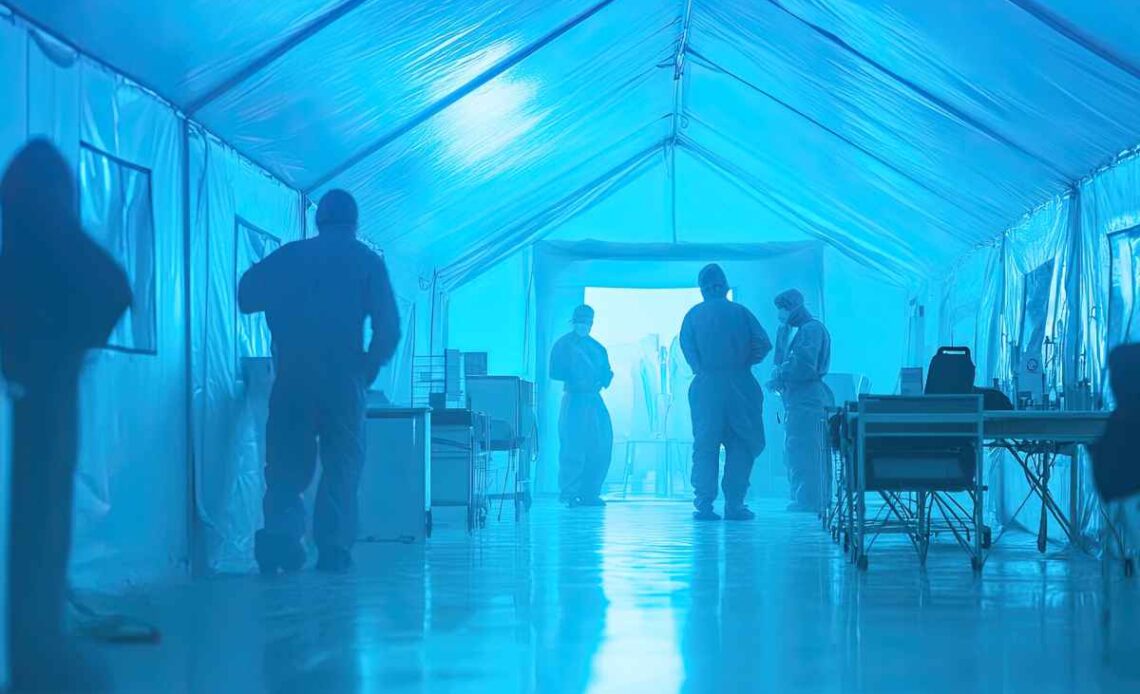
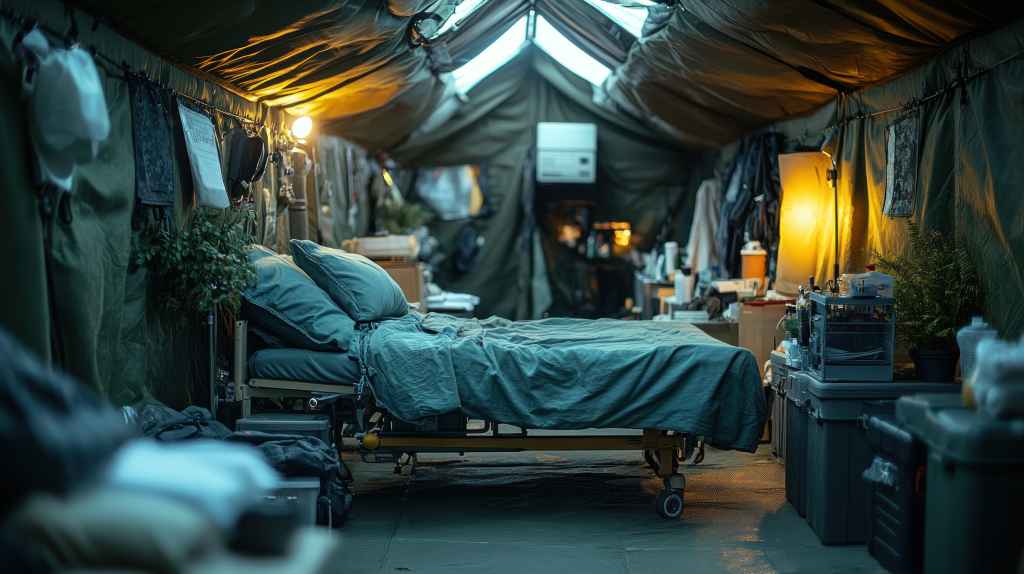
When disaster strikes—whether it’s a war, earthquake, pandemic, or refugee crisis—medical help can’t always wait for permanent facilities. That’s where field hospitals come in. These temporary medical facilities save lives in emergencies, delivering critical care when traditional hospitals are overwhelmed, damaged, or inaccessible.
But what exactly makes them so vital? Why should you care about them? This post will break it down in a way that’s clear, engaging, and practical.
What is a Field Hospital?
Field hospitals, also known as combat support hospitals (for military treatment facilities), evacuation hospitals, temporary hospitals, emergency field hospitals, and so on, are mobile and temporary medical detachments deployed quickly to provide emergency care in crisis zones.
Unlike permanent hospitals, mobile field hospitals are designed for rapid assembly, often using tents, modular containers, or repurposed buildings.
Mobile field hospitals are staffed by doctors, nurses, aid workers, and other medical personnel who deliver everything from trauma surgery and medical treatment to maternal care, depending on the emergency and available medical equipment.
They can pop up in war zones, disaster-stricken areas, medical facilities needing help during health crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic, measles outbreak, and so on, or even remote sites with no medical treatment facility.
How are Mobile Field Hospitals Different from Regular Hospitals?
Permanent hospitals have fixed locations and outpatient clinics, advanced equipment, and long-term staff.
Medical field hospital units, on the other hand, are built for speed, adaptability, and survival in harsh conditions. Top companies are available that offer field hospital solutions to those who need them. Here’s how they differ:
- Mobility: They can be packed, moved, and reassembled in merely hours or just a few days.
- Simplified Care: They focus on emergency and essential services, not long-term treatments.
- Temporary Healthcare Professionals: Medical teams in field hospital sections often rotate in short shifts due to high stress and danger. Thus, they have a limited medical response capacity.
- Resource Constraints: They work with limited medical supplies, electricity, and sometimes even clean water.
Despite these challenges, they’re lifelines when no other options exist.
When are Field Hospitals Used?
Field hospitals aren’t just for wars—they serve in multiple crisis scenarios: from natural disasters to humanitarian missions.
First, earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods can destroy local hospitals. Field units step in to treat injuries, prevent disease outbreaks, and handle surges in patients.
In battle zones, field hospitals carry out military medical operations near frontlines to stabilize wounded and gassed soldiers (even civilians) under extreme conditions.
Aside from that, field hospitals’ scalable ward spaces can aid in capacity issues during public health crises like Ebola outbreaks and so on.
Finally, field hospitals provide vaccinations, maternal health services, and emergency treatments when conducting humanitarian missions.
Without them, countless more would die waiting for help.
Who Runs Field Hospitals?
Mobile medical facilities aren’t thrown together randomly—they’re managed by highly organized groups, ranging from military forces and humanitarian organizations to national government disaster agencies and international groups. These teams train rigorously to work in chaos, making split-second decisions to save lives.
What Services Do Field Hospitals Provide?
They’re not just ‘band-aid stations;’ depending on the crisis, mobile field hospitals offer the following:
Emergency Trauma Care
Bullet wounds, burns, fractures—field surgeons operate with limited medical kits to stop bleeding and prevent fatal complications.
Basic Primary Care
Infections, dehydration, and chronic conditions (like diabetes) still need treatment, even in disasters.
Childbirth and Pediatric Care
Babies don’t wait for stable conditions. Field hospitals deliver newborns and treat malnourished children.
Disease Control
Cholera, measles, and COVID-19 spread fast in crowded camps. Isolation tents and vaccination drives curb outbreaks.
Mental Health Support
Survivors of war or disasters suffer anxiety as well as other mental health concerns. Counselors provide urgent psychological help.
The goal? Stabilize, treat, and prevent further loss of life.
What Are the Biggest Challenges Mobile Field Hospitals Face?
Mobile field hospitals aren’t perfect. They face various challenges.
Field hospitals have to deal with limited resources (shortages of blood, meds, and equipment), dangerous conditions (bombings, disease exposure, or unstable terrain), staff burnout (working nonstop in high-stress, traumatic environments can jade even the most hardworking and inspired medical personnel), and don’t forget about logistical nightmares (transporting supplies through war zones or rubble).
Yet, despite these hurdles, they persist—because giving up isn’t an option.
How Can You Support Field Hospitals?
You don’t need to be a doctor to help. Below are some ways you can lend a helping hand:
- Donate to reliable organizations that are known and verified to send out expeditionary medical facility units in distressed areas.
- Advocate for crisis preparedness. Push governments to invest in disaster response.
- Spread awareness – many people don’t know field hospitals exist until they need one.
- If you’ve got the skills, volunteer. Medical and logistics professionals are always needed.
Every bit helps. These hospitals run on humanity’s collective effort.
The Bottom Line: Why Should You Care?
Field hospitals are more than temporary tents—they’re symbols of resilience. When the world crumbles, they stand in the wreckage, pulling survivors from the brink.
They matter because anyone, anywhere, could need one someday—maybe even you.
So next time you hear about a disaster, remember: somewhere, a team is racing against time in a field hospital, fighting to keep people alive. And that’s worth knowing about.